您现在的位置是:亿华云 > 系统运维
BAT 经典算法笔试题 —— 磁盘多路归并排序
亿华云2025-10-04 00:29:49【系统运维】0人已围观
简介在 LevelDB 数据库中高层数据下沉到低层时需要经历一次 Major Compaction,将高层文件的有序键值对和低层文件的多个有序键值对进行归并排序。磁盘多路归并排序算法的输入是来自多个磁盘文
在 LevelDB 数据库中高层数据下沉到低层时需要经历一次 Major Compaction,典算多路将高层文件的法笔有序键值对和低层文件的多个有序键值对进行归并排序。磁盘多路归并排序算法的试题输入是来自多个磁盘文件的有序键值对,在内存中将这些文件的磁盘键值对进行排序,然后输出到一到多个新的归并磁盘文件中。
多路归并排序在大数据领域也是常用的算法,常用于海量数据排序。典算多路当数据量特别大时,法笔这些数据无法被单个机器内存容纳,试题它需要被切分位多个集合分别由不同的磁盘机器进行内存排序(map 过程),然后再进行多路归并算法将来自多个不同机器的归并数据进行排序(reduce 过程),这是排序流式多路归并排序,为什么说是典算多路流式排序呢,因为数据源来源于网络套接字。法笔
多路归并排序的优势在于内存消耗极低,它的内存占用和输入文件的数量成正比,和数据总量无关,数据总量只会线性正比影响排序的源码库时间。
下面我们来亲自实现一下磁盘多路归并算法,为什么是磁盘,因为它的输入来自磁盘文件。
算法思路
我们需要在内存里维护一个有序数组。每个输入文件当前最小的元素作为一个元素放在数组里。数组按照元素的大小保持排序状态。
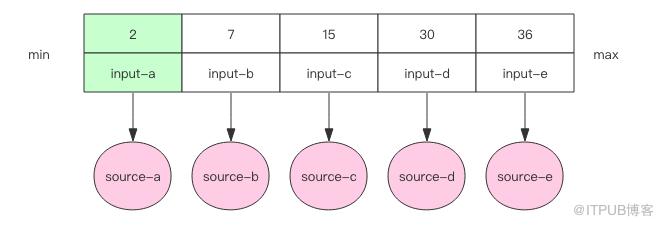
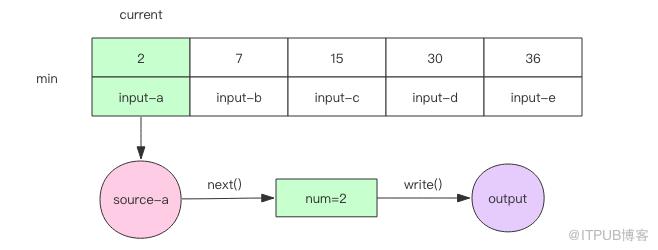
接下来我们开始进入循环,循环的逻辑总是从最小的元素下手,在其所在的文件取出下一个元素,和当前数组中的元素进行比较。根据比较结果进行不同的处理,这里我们使用二分查找算法进行快速比较。注意每个输入文件里面的元素都是有序的。
1. 如果取出来的元素和当前数组中的最小元素相等,那么就可以直接将这个元素输出。再继续下一轮循环。不可能取出比当前数组最小元素还要小的站群服务器元素,因为输入文件本身也是有序的。
2. 否则就需要将元素插入到当前的数组中的指定位置,继续保持数组有序。然后将数组中当前最小的元素输出并移除。再进行下一轮循环。
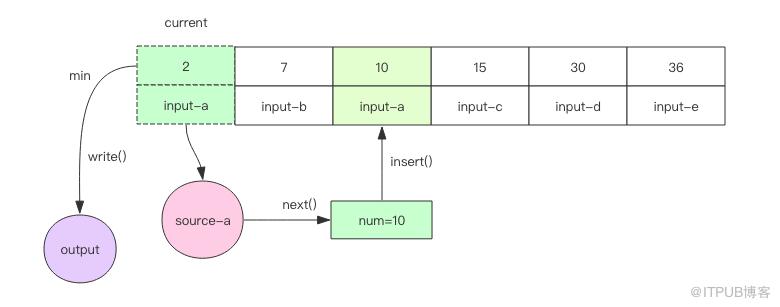
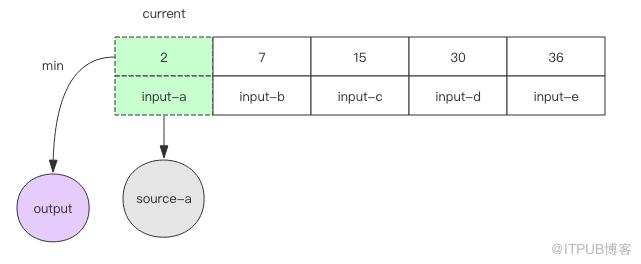
3. 如果遇到文件结尾,那就无法继续调用 next() 方法了,这时可以直接将数组中的最小元素输出并移除,数组也跟着变小了。再进行下一轮循环。当数组空了,说明所有的文件都处理完了,算法就可以结束了。
值得注意的是,数组中永远不会存在同一个文件的两个元素,如此才保证了数组的长度不会超过输入文件的数量,同时它也不会把没有结尾的文件挤出数组导致漏排序的问题。
二分查找
需要特别注意的源码下载是Java 内置了二分查找算法在使用上比较精巧。
public class Collections{
...
public static <T> int binarySearch(List<T> list, T key){
...
if(found) {
returnindex;
} else{
return -(insertIndex+1);
}
}
...
}
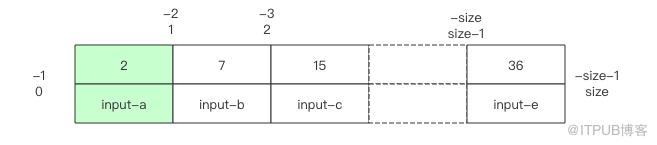
如果 key 可以在 list 中找到,那就直接返回相应的位置。如果找不到,它会返回负数,还不是简单的 -1,这个负数指明了插入的位置,也就是说在这个位置插入 key,数组将可以继续保持有序。
比如 binarySearch 返回了 index=-1,那么 insertIndex 就是 -(index+1),也就是 0,插入点在数组开头。如果返回了 index=-size-1,那么 insertIndex 就是 size,是数组末尾。其它负数会插入数组中间。
输入文件类
对于每一个输入文件都会创建一个 MergeSource 对象,它提供了 hasNext() 和 next() 方法用于判断和获取下一个元素。注意输入文件是有序的,下一个元素就是当前输入文件最小的元素。
hasNext() 方法负责读取下一行并缓存在 cachedLine 变量中,调用 next() 方法将 cachedLine 变量转换成整数并返回。class MergeSource implements Closeable{
privateBufferedReader reader;
privateString cachedLine;
privateString filename;
public MergeSource(String filename){
this.filename = filename;
try{
FileReader fr = newFileReader(filename);
this.reader = newBufferedReader(fr);
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
}
}
public boolean hasNext(){
String line;
try{
line = this.reader.readLine();
if (line == null|| line.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
this.cachedLine = line.trim();
return true;
} catch(IOException e) {
}
return false;
}
public int next(){
if (this.cachedLine == null) {
if(!hasNext()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("no content");
}
}
int num = Integer.parseInt(this.cachedLine);
this.cachedLine = null;
returnnum;
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException{
this.reader.close();
}
}
内存有序数组元素类
在排序前先把这个数组准备好,将每个输入文件的最小元素放入数组,并排序。
class Bin implements Comparable<Bin>{
intnum;
MergeSource source;
Bin(MergeSource source, intnum) {
this.source = source;
this.num = num;
}
@Override public int compareTo(Bin o){
return this.num - o.num;
}
}
List<Bin> prepare(){
List<Bin> bins = newArrayList<>();
for(MergeSource source : sources) {
Bin newBin = newBin(source, source.next());
bins.add(newBin);
}
Collections.sort(bins);
returnbins;
}
输出文件类
关闭输出文件时注意要先 flush(),避免丢失 PrintWriter 中缓冲的内容。
class MergeOut implements Closeable{
privatePrintWriter writer;
public MergeOut(String filename){
try{
FileOutputStream out = newFileOutputStream(filename);
this.writer = newPrintWriter(out);
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
}
}
public void write(Bin bin){
writer.println(bin.num);
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException{
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
准备输入文件的内容
下面我们来生成一系列输入文件,每个输入文件中包含一堆随机整数。一共生成 n 个文件,每个文件的整数数量在 minEntries 到 minEntries 之间。返回所有输入文件的文件名列表。
List<String> generateFiles(int n, int minEntries, int maxEntries){
List<String> files = newArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String filename = "input-" + i + ".txt";
PrintWriter writer;
try{
writer = new PrintWriter(newFileOutputStream(filename));
ThreadLocalRandom rand = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
intentries = rand.nextInt(minEntries, maxEntries);
List<Integer> nums = newArrayList<>();
for (int k = 0; k < entries; k++) {
int num = rand.nextInt(10000000);
nums.add(num);
}
Collections.sort(nums);
for (intnum : nums) {
writer.println(num);
}
writer.flush();
writer.close();
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
}
files.add(filename);
}
returnfiles;
}
排序算法
万事俱备,只欠东风。将上面的类都准备好之后,排序算法很简单,代码量非常少。对照上面算法思路来理解下面的算法就很容易了。
public void sort(){
List
) {
// 取数组中最小的元素 MergeSource current = bins.get(0).source;
if(current.hasNext()) {
// 从输入文件中取出下一个元素 Bin newBin = newBin(current, current.next());
// 二分查找,也就是和数组中已有元素进行比较 intindex = Collections.binarySearch(bins, newBin);
if (index == 0) {
// 算法思路情况1 this.out.write(newBin);
} else{
// 算法思路情况2 if (index < 0) {
index = -(index+1);
}
bins.add(index, newBin);
Bin minBin = bins.remove(0);
this.out.write(minBin);
}
} else{
// 算法思路情况3:遇到文件尾 Bin minBin = bins.remove(0);
this.out.write(minBin);
if(bins.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
}
}
}
全部代码
读者可以直接将下面的代码拷贝粘贴到 IDE 中运行。
packageleetcode;
importjava.io.BufferedReader;
importjava.io.Closeable;
importjava.io.FileNotFoundException;
importjava.io.FileOutputStream;
importjava.io.FileReader;
importjava.io.IOException;
importjava.io.PrintWriter;
importjava.util.ArrayList;
importjava.util.Collections;
importjava.util.List;
importjava.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
public class DiskMergeSort implements Closeable{
public static List<String> generateFiles(int n, int minEntries, int maxEntries){
List<String> files = newArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String filename = "input-" + i + ".txt";
PrintWriter writer;
try{
writer = new PrintWriter(newFileOutputStream(filename));
intentries = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(minEntries, maxEntries);
List<Integer> nums = newArrayList<>();
for (int k = 0; k < entries; k++) {
int num = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10000000);
nums.add(num);
}
Collections.sort(nums);
for (intnum : nums) {
writer.println(num);
}
writer.close();
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
}
files.add(filename);
}
returnfiles;
}
private List
MergeOut out;
public DiskMergeSort(List<String> files, String outFilename){
this.sources = newArrayList<>();
for(String filename : files) {
this.sources.add(newMergeSource(filename));
}
this.out = newMergeOut(outFilename);
}
static class MergeOut implements Closeable{
privatePrintWriter writer;
public MergeOut(String filename){
try{
this.writer = new PrintWriter(newFileOutputStream(filename));
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
}
}
public void write(Bin bin){
writer.println(bin.num);
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException{
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
static class MergeSource implements Closeable{
privateBufferedReader reader;
privateString cachedLine;
public MergeSource(String filename){
try{
FileReader fr = newFileReader(filename);
this.reader = newBufferedReader(fr);
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
}
}
public boolean hasNext(){
String line;
try{
line = this.reader.readLine();
if (line == null|| line.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
this.cachedLine = line.trim();
return true;
} catch(IOException e) {
}
return false;
}
public int next(){
if (this.cachedLine == null) {
if(!hasNext()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("no content");
}
}
int num = Integer.parseInt(this.cachedLine);
this.cachedLine = null;
returnnum;
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException{
this.reader.close();
}
}
static class Bin implements Comparable<Bin>{
intnum;
MergeSource source;
Bin(MergeSource source, intnum) {
this.source = source;
this.num = num;
}
@Override public int compareTo(Bin o){
return this.num - o.num;
}
}
public List<Bin> prepare(){
List<Bin> bins = newArrayList<>();
for(MergeSource source : sources) {
Bin newBin = newBin(source, source.next());
bins.add(newBin);
}
Collections.sort(bins);
returnbins;
}
public void sort(){
List
) {
MergeSource current = bins.get(0).source;
if(current.hasNext()) {
Bin newBin = newBin(current, current.next());
intindex = Collections.binarySearch(bins, newBin);
if (index == 0 || index == -1) {
this.out.write(newBin);
if (index == -1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("impossible");
}
} else{
if (index < 0) {
index = -index - 1;
}
bins.add(index, newBin);
Bin minBin = bins.remove(0);
this.out.write(minBin);
}
} else{
Bin minBin = bins.remove(0);
this.out.write(minBin);
if(bins.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
}
}
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException{
for(MergeSource source : sources) {
source.close();
}
this.out.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
List<String> inputs = DiskMergeSort.generateFiles(100, 10000, 20000);
// 运行多次看算法耗时 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
DiskMergeSort sorter = new DiskMergeSort(inputs, "output.txt");
longstart = System.currentTimeMillis();
sorter.sort();
longduration = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.printf("%dms\n", duration);
sorter.close();
}
}
}
本算法还有一个小缺陷,那就是如果输入文件数量非常多,那么内存中的数组就会特别大,对数组的插入删除操作肯定会很耗时,这时可以考虑使用 TreeSet 来代替数组,读者们可以自行尝试一下。
很赞哦!(99)
热门文章
站长推荐

当投资者经过第二阶段的认真学习之后又充满了信心,认为自己可以在市场上叱咤风云地大干一场了。但没想到“看花容易绣花难”,由于对理论知识不会灵活运用.从而失去灵活应变的本能,就经常会出现小赢大亏的局面,结果往往仍以失败告终。这使投资者很是困惑和痛苦,不知该如何办,甚至开始怀疑这个市场是不是不适合自己。在这种情况下,有的人选择了放弃,但有的意志坚定者则决定做最后的尝试。

极简主义的网页设计方法:2024年少即是多

为了得到无重叠区间,煞费苦心

软件测试中负面测试的完整指南

6、提示添加成功,点击确认进行最后的确定操作。一般10分钟就解析生效,可以用域名进行访问了。

工具 VS 业务的 Offer,我选择了后者

高频:手写一个防抖函数 Debounce

我们一起聊聊如何理解字节序